Interprocess Communication - Distributed Systems
- Message passing interface
- Supports point to point and collective communication
- Goals are High performance, Scalability, Portability
- Dominant in HPC (High performance computing)
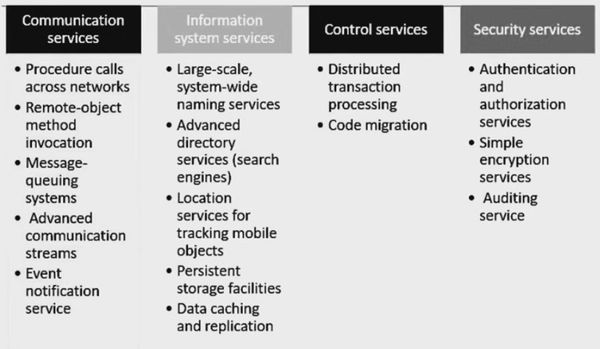
- Middleware Services
- Software layer situated between software and operating system
- Provides services that help in communication between components in DS
- Types of communication
- Synchronous communication
- Client sends request to server and waits for response
- Types
- RPC (Remote Procedure Call)
- Protocol that a program can use to request a service from a program from a program located in another computer on a network without having to understand the network detail
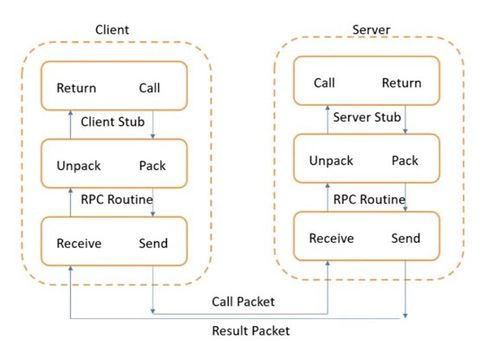
- Steps
- Client procedure calls client stub in a normal way
- Client stub builds message, calls local OS
- Client OS sends message to local OS
- Remote OS gives message to Server stub
- Server stub unpacks parameters, calls server
- Server does work, returns result to the stub
- Server stub packs it in message, calls local OS
- Server OS sends message to client OS
- Client OS gives message to client stub
- Stub unpacks result, returns to client
- Components
- Client
- Client stub
- RPC Routine
- Handle transmission of message between client and server
- Server stub
- RMI (Remote Method Invocation)
- Set of protocols being developed that enables java objects to communicate remotely with other java objects
- All objects must be written in Java
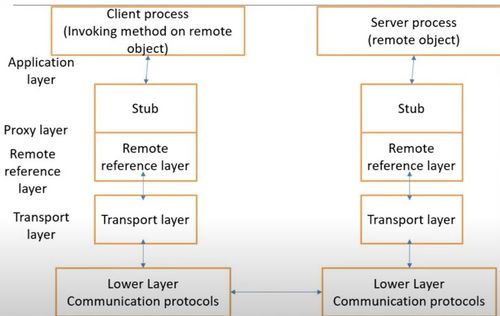
- Characteristics of Java objects
- Simple protocol as compared to COBRA & DCOM
- Works only with java objects as compared to COBRA & DCOM
- Based on RPC
- Goals
- Seamless object remote invocation
- Callbacks from server to client
- Distributed garbage collection
- RPC (Remote Procedure Call)
- Asynchronous communication
- Client sends request to server but doesn't waits for response and keeps doing other tasks
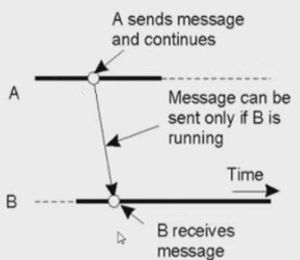
- Transient communication
- Both client and server needs to be active for communication
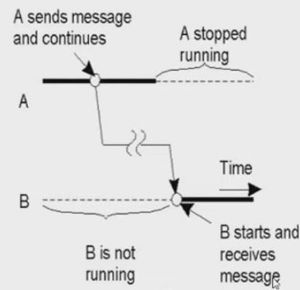
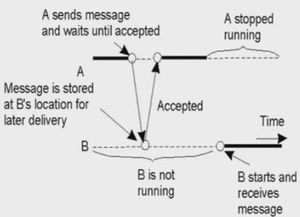
- Persistent communication
- Both client and server doesn't needs to be active for communication
- Synchronous communication
- Classification
- Message Oriented Communication
- Way of communication between the processes on the sender and receiver machine
- Classification
- Types of Message Oriented
- Persistent Asynchronous communication
- Persistent Synchronous communication
- Transient Asynchronous communication (One way RPC)
- Transient Synchronous communication
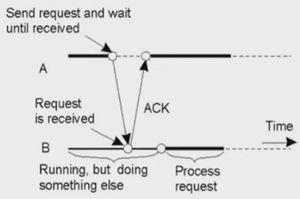
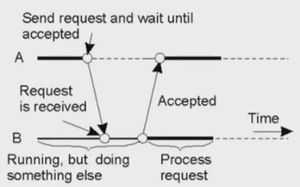
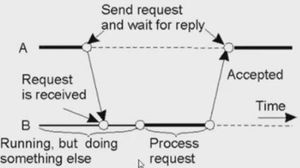
- Receipt-based transient Synchronous communication
- Delivery-based transient Synchronous communication at message delivery (Asynchronous RPC)
- Response-based transient Synchronous communication (RPC)
- Receipt-based transient Synchronous communication
- Persistent Asynchronous communication
- Stream Oriented Communication
- Form of communication in which timing plays a crucial role
- Transmission Modes
- Synchronous
- Specifies max end to end delay variance between teo packets is ok
- Asynchronous
- End to end delay can be maximum (no effect of time)
- Isochronous
- Max end to end delay is specified and variance to 0
- Synchronous
- Algorithm
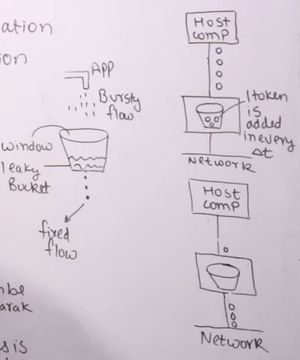
- Leaky bucket
- Open bucket
- Leaky bucket
- Difference


- Trick: Sexy Senorita Ranawaywith CAR OF Police Department
- Message Oriented Communication
- Group Communication
- Modes
- Unicast
- Point to Point (1 to 1)
- Anycast
- 1 to nearest 1 of several identical nodes
- Netcast
- 1 to many (1 at a time)
- Multicast
- 1 to many
- Broadcast
- 1 to all
- Unicast
- Types
- One to Many (Single sender and Multiple receivers)
- Receiver processes messages from group
- Closed group vs Open group
- Peer group vs Hierarchical group
- Many to One (Multiple senders and Single receiver)
- Many senders send the message to selective receiver
- Uses buffer to control incoming messages
- Receiver can be selective or non selective
- Selective
- Specifies a unique sender, the message exchange takes place only if that sender sends the message
- Non Selective
- Specifies a set of sender and if any one sender in the set sends a message to this receiver message exchange takes place
- Selective
- Many to Many (Multiple senders and Multiple receivers)
- Many senders sends messages to many receivers
- Semantics ordered message delivery are
- Absolute ordering
- All messages delivered to all receivers exactly in the way that they are sent
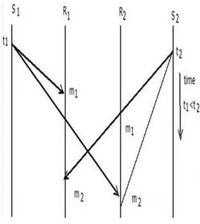
- Consistent ordering
- The message is delivered to all receivers possessing the same order
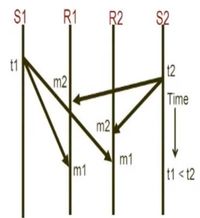
- Casual ordering
- Events of sending messages are linked, messages are received in same order as sent
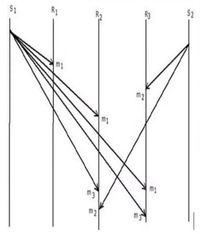
- Absolute ordering
- One to Many (Single sender and Multiple receivers)
- Modes