Sql - D B M S
- DBMS
- RDBMS
- Structure
- Database > Tables > Columns > Rows
- Language
- SQL (Structured Query Language)
- NoSQL
- XML Model
- Structure
- Language
- Document type definition (DTD)
- SQL
- Used to access and manipulate data
- SQL used CRUD operations to communicate with DB
- SQL is not DB, is a query language
- RDBMS (Relational Database Management System)
- Software that enable us to implement designed relational model
- Eg: MySQL, MS SQL, Oracle, IBM
- Table/Relation is the simplest form of data storage object in R-DB
- Data Types
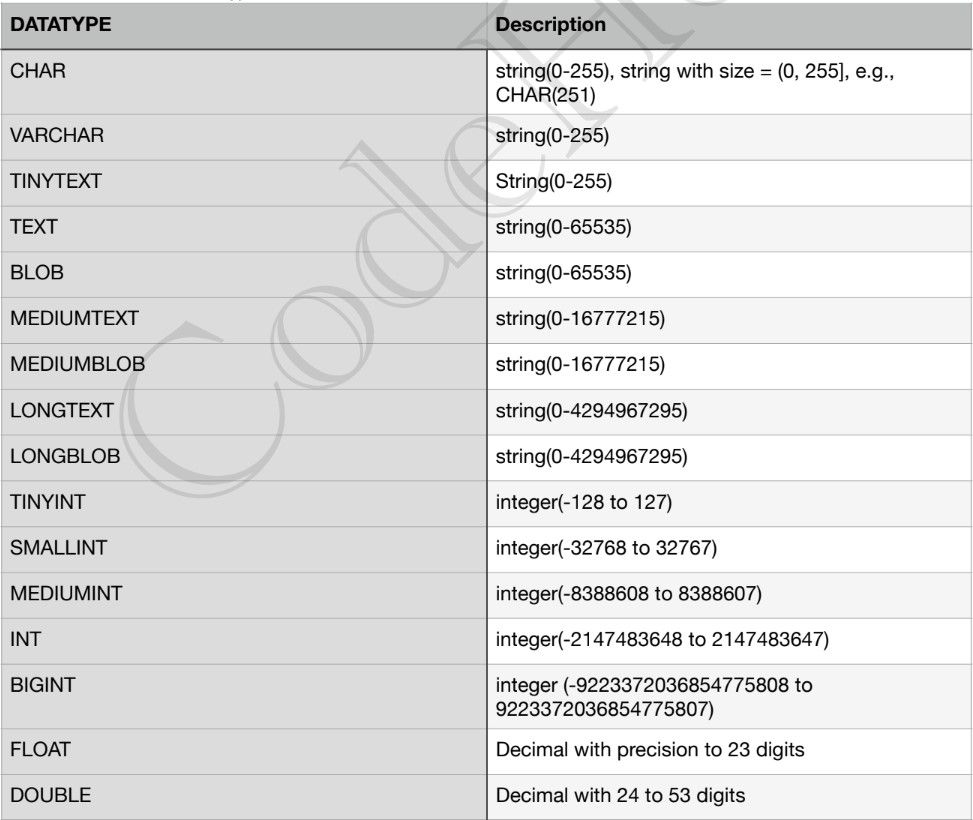
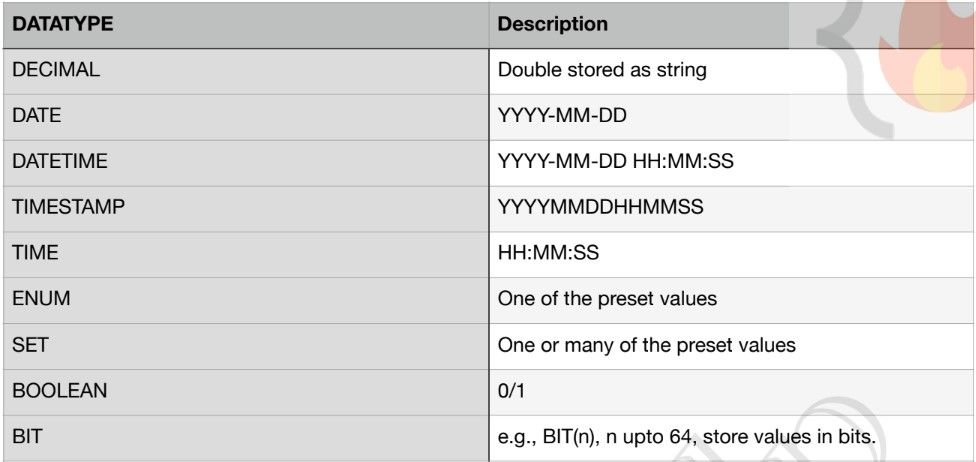
- Size => TINY < SMALL < MEDIUM < INT < BIGINT
- Values can also be unsigned => INT UNSIGNED
- Types of SQL commands
- DDL (data definition language) => Defining relation schema
- CREATE => create table, DB, view
- ALTER TABLE => Modification in table structure
- DROP => Delete table, DB, view
- TRUNCATE => Remove all the tuples from the table
- RENAME => Rename DB name, table name, column name etc
- DRL/DQL (data retrieval language / data query language) => Retrieve data from the tables
- DML (data modification language) => Use to perform modifications in the DB
- INSERT => Insert data into a relation
- UPDATE => Update relation data
- DELETE => Delete row(s) from the relation
- DCL (Data Control language) => Grant or revoke authorities from user
- GRANT => Access privileges to the DB
- REVOKE => revoke user access privileges
- TCL (Transaction control language) => To manage transactions done in the DB
- START TRANSACTION => Begin a transaction
- COMMIT => Apply all the changes and end transaction
- ROLLBACK => discard changes and end transaction
- SAVEPOINT => Checkout within the group of transactions in which to rollback
- Legacy Data Model
- Network Model
- Hierarchical Model
- Table Options
- Design Mode => Column Attributes
- Column
- Datatype
- Primary Key
- Not NULL
- Auto Increment
- Default/Expression
- View table
- Operators
- Arithmetic => +, -, *, /, %
- Comparison => >, >=, <, <=, =, !=, <>
- Logical => AND, OR, NOT, IN, BETWEEN
- LIKE => %, _
- REGEXP => ^, $, |, [ ], [-]
Query Processing
- Translating SQL Queries into Relational Algebra => Procedural / Formal Query Language => Mathematical Form / Representation before SQL
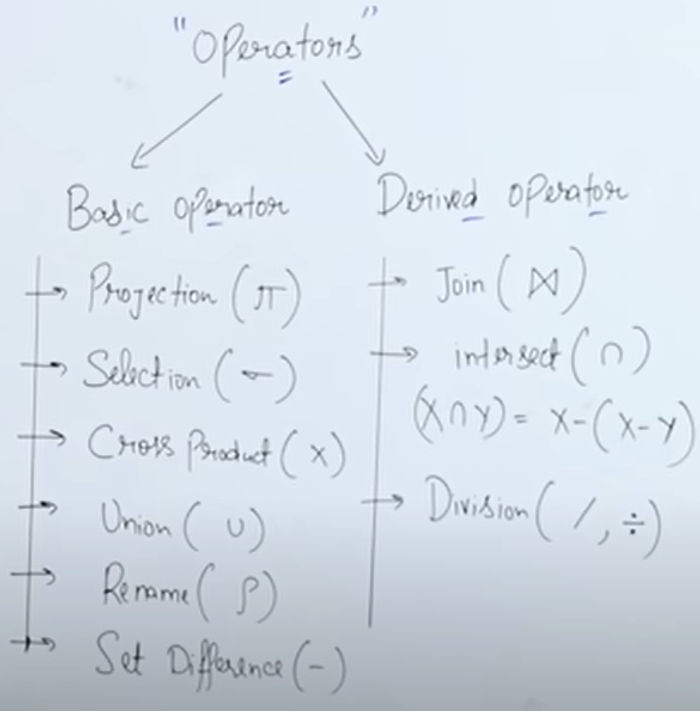
- Projection => ⊓colName1(tableName1)
- Retrieve Column Data, Returns Unique values or Unique combination of Values, Used at last
- Selection => ⊓colName1(σcolumnName2="value"(tableName1))
- Cross Product/ Cross Join => tableName1 x tableName2
- Both Table can be same
- Total no. of Columns after Cross Product will be sum of Columns of both Table & Row will be product of Rows of both Table
- Union => (tableName1 U tableName2) => (⊓colName1(tableName1) U ⊓columnName2(tableName2))
- No. of Columns must be same, Domain of every Column must be same, Not Commutative, Column name will be from colName1
- Rename
- Set Difference => (tableName1 * tableName2) = (tableName1 Ո tableName2')
- A but not B, No. of Columns must be same, Domain of every Column must be same, Commutative
- Join (⋈) => Used when Query is required between 2 Tables => Tables must have a common Attribute => Cross Product + Condition
- Natural Join => SELECT colName1 FROM tableName1 NATURAL JOIN tableName2
- Conditional Join
- Equi Join
- Self Join
- Outer Join
- Left => Gives matching Rows & The Rows which are in the Left Table
- Right => SELECT colName1 FROM tableName1 RIGHT OUTER JOIN tableName2 ON (tableName1.columnName = tableName2.columnName)
- Gives matching Rows & The Rows which are in the Right Table
- Full => Union of Left & Right
- Intersect
- Division => tableName1(colName1, columnName2) / tableName2(columnName2)
- Used for every/ all Query, It returns "x" values for which there exists tuple <x, y> for every "y" value in tableName2
- Relational Calculus
- Domain Relational Calculus => Focus on Columns/ Attributes
- Tuple Relational Calculus
- Non-Procedural Query language unlike Relational Algebra
- Focus on Rows/ Tuples => {t | p(t)} => {Resulting Tuples | Predicate Condition}
- Operations => Atomic Functions => OR, AND, NOT
- Optimization
- Heuristic Query Optimization
- Cost based Query Optimization


